Introducing a preview of SAFe 5
Why is this update important?
What is business agility?
- Business agility lets you capitalize on emerging opportunities by empowering you to make quick decisions, allocate money, and align the right people to do the work. SAFe® 5 has the guidance to help you get there.
- What began in software development is expanding to encompass the entire enterprise, changing how people work and how every aspect of the business is run. We're now in the age of software-an interconnected, real-time world where every industry is a tech-enabled industry and every company is, at least in part, a software company. Organizations that master business agility are the ones that will thrive-not just survive.
- Business agility happens when the entire organization-business and tech leaders, compliance, development, finance, legal, marketing, operations, sales, security, support-uses Lean and Agile practices to continually and proactively deliver innovative bbusiness solutions faster than the competition.
- With guidance from SAFe® 5, you can become the Agile business you need to be and win in the digital age. But the Framework by itself can't orchestrate your transformation; It's your people-teams and leaders-who make it happen. When agility permeates your organization, you can quickly adapt to new, macro conditions in your industry. Respond to new, competitive threats. Efficiently identify and deliver incremental customer value. Maintain quality in an evolving product and solution portfolio. Reconfigure teams and redeploy talent in response to changing business needs. In short: thrive in fast-moving markets.
Globalization, fast-moving markets, disruption, the unprecedented pace of technological innovation. Organizations know that they need to transform-now-to compete. But their existing business models, organizational hierarchy, and technology infrastructure simply can't keep up with how quickly the company needs to adap.
Agile product delivery isn't enough. You need business agility.
Introducing the Seven Core Competencies of the Lean Enterprise





SAFe® 5 is built around the Seven Core Competencies of the Lean Enterprise. There competencies include major rewrites to the orginal five competencies introduced in SAFe 4.6, along with two entirely new competencies-Organizational Agility and Continuous Learning Culture. The competencies are the primary leans for understanding and implementing SAFe, as illustrated in the Overview tab on the Big Picture. Each competency is a set of related knowledge, skills, and behaviors that together, enable enterprises to achieve business agility by delivering the best quality and value in shortest sustainable lead time. Each competency is summarized below.
Team and Technical Agility describes the critical skills and Lean-Agile principles and practices that high-performing Agile teams and teams of Agile teams use to create high-quality solutions for their customers. The result is increased productivity, better quality, faster time-to-market, and predictable delivery of value.
Agile Product Delivery is a customer-centric approach to defining, building, and releasing a continuous flow of valuable products and services to customers and users. This enables the organization to provide solutions that delight customers, lower development costs, reduct risk and outmaneuver the competition.

Lean-Agile Leadership describes how Lean-Agile leaders drive and sustain organizational change by empowering individuals and teams to reach their highest potential. They do this through leading by example, adopting a Lean-Agile mindset, and leading the change to a new way of working. The result is more engaged employees, increased productivity and innovation, and successful organizational change.
Enterprise Solution Delivery describes how to apply Lean-Agile principles and practices to the specification, development, deployment, operation, and evolution of the world's largest and most sophisticated software applications, networks, and cyber-physical systems.
Lean Portfolio Management aligns stategy and execution by applying Lean and systems thinking approaches to strategy and investment funding, Agile portfolio operations, and governance. These collaborations give the enterprise the ability to align strategy to execution, to meet existing commitments reliably, and to better enable innovation.
Organizational Agility describes how Lean-thinking people and Agile teams optimize their business processes, evolve strategy with clear and decisive new commitments, and quickly adapt the organization as needed to capitalize on new opportunities.
Continuous Learning Culture describes a set of values and practices that encourage individuals-and the enterprise as a whole-to continually increase knowledge, competence, performance, and innovation. This is achieved by becoming a learning organization, committing to relentless improvement, and promoting a culture of innovation.
What' New in SAFe® 5?
On behalf of the entire Scaled Agile team and the SAFe Contributors, we are delighted to announce a preview of SAFe® 5 for Lean Enterprises, which introduces the Seven Core Competencies of the Lean Enterprise necessary to achieve true business agility.
We're now in the age of software-an interconnected, real-time world where every industry is powered by technology and every company is, at least in part, a software company. Organizations that master Business Agility are the ones that will thrive-not just survive. Business Agility happens when the entire organization uses Lean and Agile practices to continually and proactively deliver innovative business solutions faster than the competition. This new release is designed to expand SAFe to encompass the entire enter prise and enable business agility.
Below are the highlights of the What's New in SAFe® 5.
New Big Picture
As you can see from below, SAFe® 5 has a new Big Picture with an improved look and feel. Figure 1 show the Full SAFe configuration with the Key changes highlighted with red boxes.

Figure 1. SAFe® 5 Big Picture Changes
New Business Agility
Business Agility is the ability to compete and thrive in the digital age by quickly responding to market changes and emerging opportunities with innovative business solutions. It requires that everyone involved in delivering solutions-business and technology leaders, development, IT operation, legal, marketing, finance, support, compliance, security, and others-use Lean and Agile practices to continually deliver innovative, high-quality products and services faster than the competition.
SAFe offers a way (Figure 2) around value streams in steadof departments. This model, which Kotter calls a 'dual operating system.' restores the speed and innovation of the entrepreneurial network while leveraging the benefits and stability of the hierarchical system.

Figure 2. SAFe as a second organizational operating system to achieve business agility
New SAFe Overview
A new overview tab (Figure 3) on the home page illustrates SAFe's seven core competencies that enable business agility. This araphic provides a simplified view of SAFe's Seven Core Competencies of the Lean Enterprise and their twenty-one dimensions that enable business agility.
The execution-related competencies are shown the left, thile the competencies that support strategy development are on the right. The Lean-Agile Leadership competency which is the foundation is in the bottom m iddle. The customer is prominently featured at the center as the focal point for all the competencies. Measure and Grow at the top right is a reminder of the importance of periodic self-assessments to track the organization's progress towards the principles and practices that enable business agility.
Moreoverm this overview is a useful tool for providing an initial orientation to SAFe, as well as an introduction to the business agility assessment, and for framing conversations with senior leaders.

Figure 3. SAFe Overview
Measuring Business Agility
The new Measure and Grow article describes how to measure the state of business agility and how to accelerate growth to improve overall economic outcomes. Portfolio leaders and the Lean-Agile Center of Excellence (LACE), now have a way to self-assess their progress on this journey.
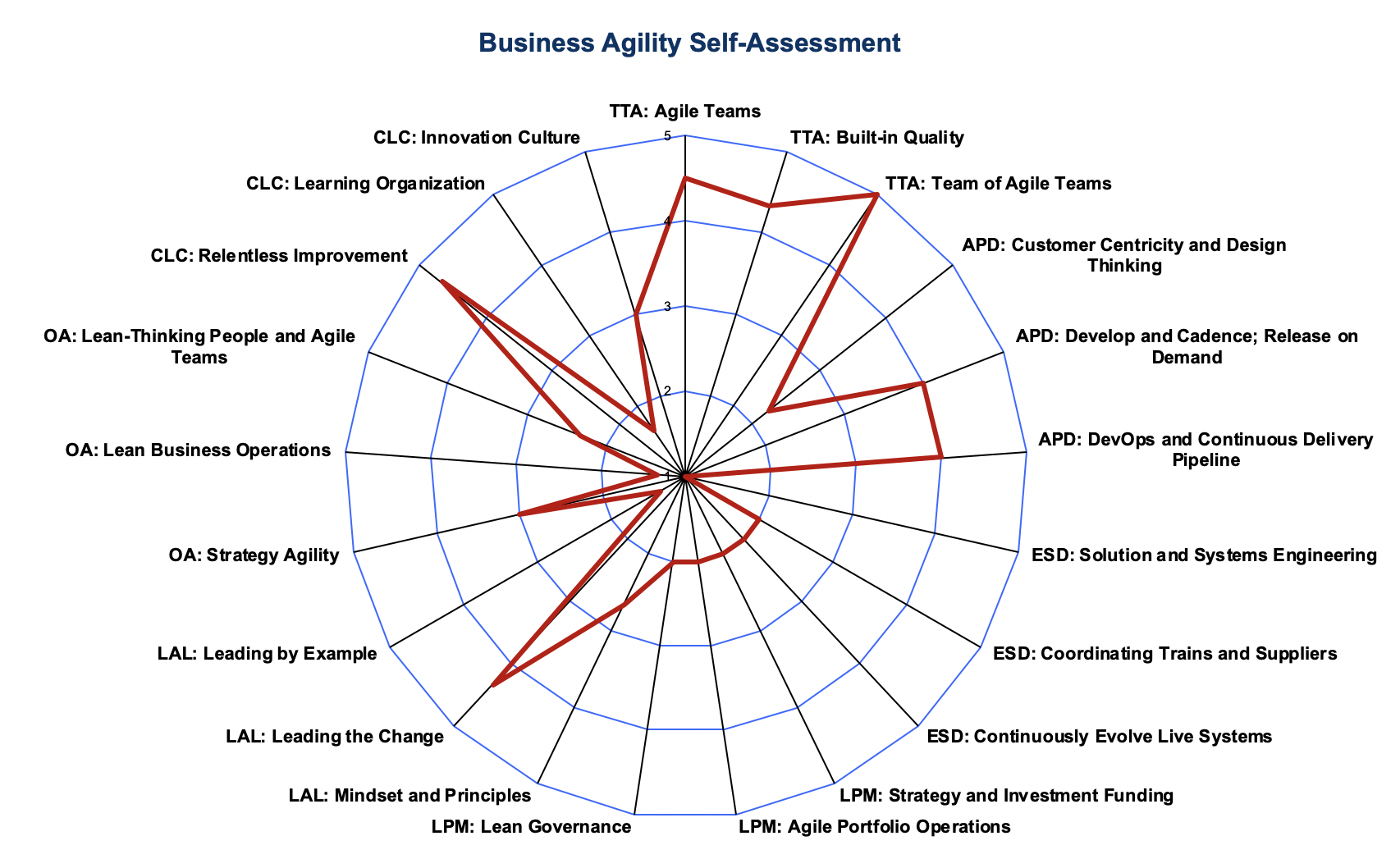
Figure 4. Measuring Business Agility
SAFe® 5 introduces two new competencies, Continuous Learning Culture, and Organizational Agility. Each is briefly described next.
1. Continuous Learning Culture.

The Continuous Learning Culture competency describes a set of values and practices that encourage individuals-and the enterprise as a whole-to continually increase knowledge, competence, performance, and innovation. This culture is achieved by becoming a learning organization, committing to relentless improvement, and promoting a culture of innovation.
This new article describes the three dimensions of a continuous learning culture:
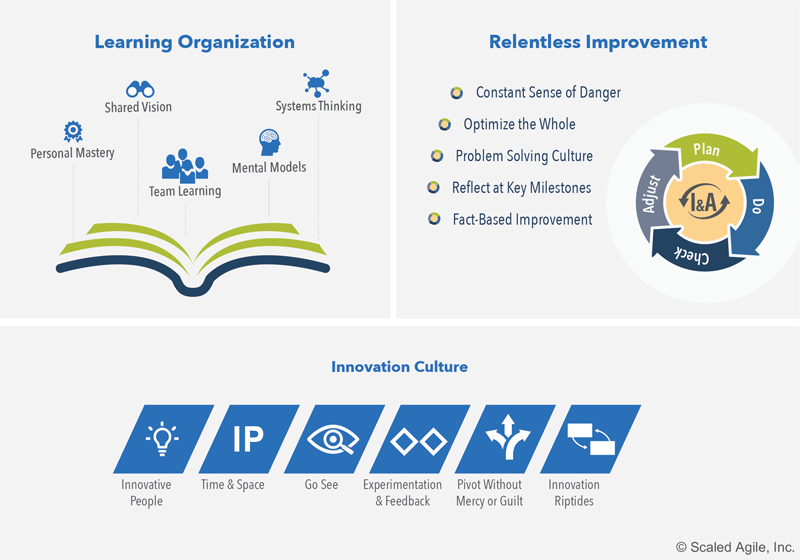
Figure 5. Continuous learning culture competency
- Learning Organization - Employees at every level are learning and growing so that the organization can transorm and adapt to an ever-changing world.
Two new Competencies
- Innovation Culture - Employees are encouraged and empowered to explore and implement creative ideas that enable future value delivery.
- Relentless Improvement - Every part of the enterprise focuses on continuously improving its solutions, products, and processes.
2. Organizational Agility
The Organizational Agility competency describes how Lean-thinking people and Agile teams optimize their business processes, evolve strategy with clear and decisive new commitments, and quickly adapt the organization as needed to capitalize on new opportunities.
This new article describes the three dimensions of organizational agility:


Figure 6. Organizational agility competency
- Lean-Thinking People and Agile Teams - Everyone involved in solution delivery is trained in Lean and Agile methods and embraces and embodies the values, principles, and practices.
- Lean Business Operations- Teams apply Lean principles to understand, map, and continuously improve the business processes that support the businesses products and services.
- Strategy Agility- The enterprise is Agile enough to continuously sense the market, and quickly change strategy when necessary.
Five Restructured Competencies
1. Team and Technical Agility

The Team and Technical Agility competency describes the critical skills and Lean-Agile principles and practices that high-performing Agile teams and Teams of Agile teams use to create high-quality solutions for their customers. The result is increased productivity, better quality, faster time-to-market, and predictable delivery of value.
This competency has been rewritten and is now organized into the following dimensions:

Figure 7. Team and technical agility competency
- Agile Teams - High-performing, cross-functional teams anchor the competency by applying effective Agile principles and practices.
- Teams of Agile Teams - Agile teams operate within the context of a SAFe Agile Release Train (ART), a long-lived, team of Agile teams that provides a shared vision and direction and is ultimately responsible for delivering solution outcomes.
- Teams of Agile Teams - Agile teams operate within the context of a SAFe Agile Release Train (ART), a long-lived, team of Agile teams that provides a shared vision and direction and is ultimately responsible for delivering solution outcomes.
2. Agile Product Delivery

The Agile Product Delivery competency is a customer-centric approach to defining, building, and releasing a continuous flow of valuable products and services to customers and users. This competency enables the organization to provide solutions that delight customers. lower development costs, reduce risk, and outmaneuver the competition.
The DevOps and Release on Demand competency has been renamed to Agile Product Delivery and expands its guidance to include the following new dimensions:
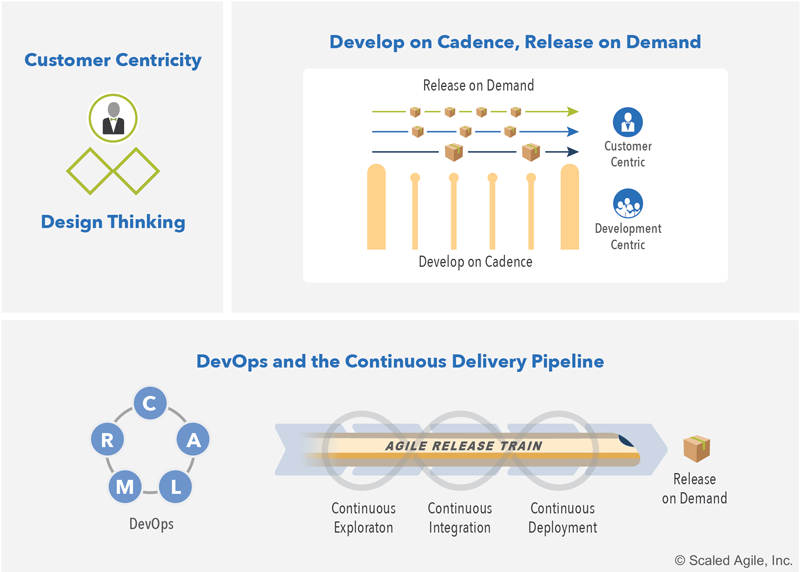
- Customer Centricity and Design Thinking - Customer centricity puts the customer at the center of every decision and uses design thinking to ensure the solution is desirable, feasible, viable, and sustainable.
- Develop on Cadence; Release on Demand - Developing on cadence helps manage the variability inherent in product development. Decoupling the release of value assures customers can get what they need when they need it.
- Develop on Cadence; Release on Demand - Developing on cadence helps manage the variability inherent in product development. Decoupling the release of value assures customers can get what they need when they need it.
3. Lean Protfolio Management
The Lean Portfolio Management competency aligns strategy and execution by applying Lean and systems thinking approaches to strategy and investment funding, Agile portfolio operations, and governance.
These collaborations give the enterprise the ability to align strategy to execution, to meet existing commitments reliably, and to better enable innovation.
This competency has been rewritten and is now organized into the following dimensions:

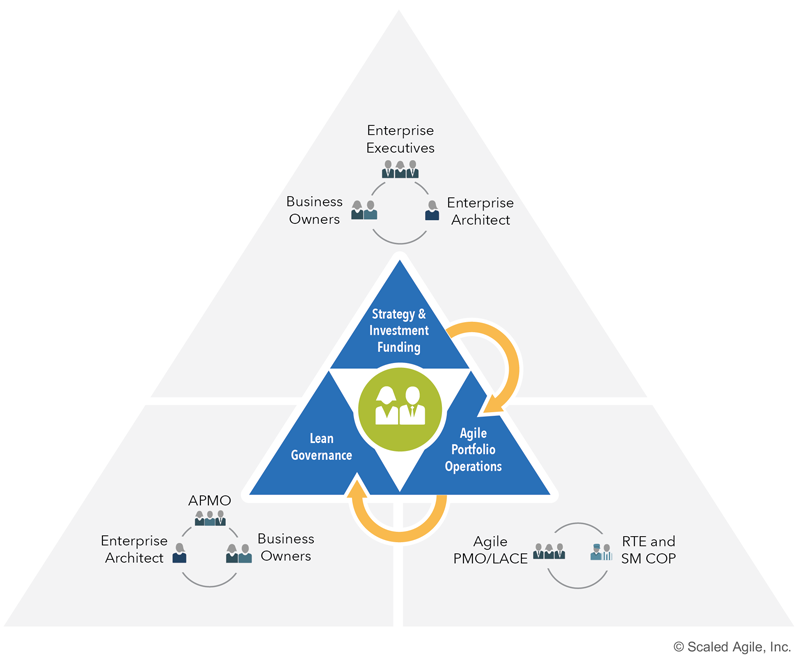
Figure 8. Agile Product Delivery competency
Figure 9. Lean Portfolio Management competency
- Strategy & Investment Funding - ensures the entire portfolio is aligned and funded to create and maintain the solutions needed to meet business targets.
- Agile Portfolio Operations - coordinates and supports decentralized program execution and fosters operational excellence.
- Lean Governance - is the oversight and decision-making of spending, audit and compliance, forecasting expenses, and measurement.
4. Enterprise Solution Delivery
The Enterprise Solution Delivery competency describes how to apply Lean-Agile principles and practices to the specification, development, deployment, operation, and evolution of the world's largest and most sophisticated software applications, networks, and cyber-physical systems.
The Business Solutions and Lean Systems Engineering competency has been renamed to Enterprise Solution Delivery and expands its guidance to include the following new dimensions:

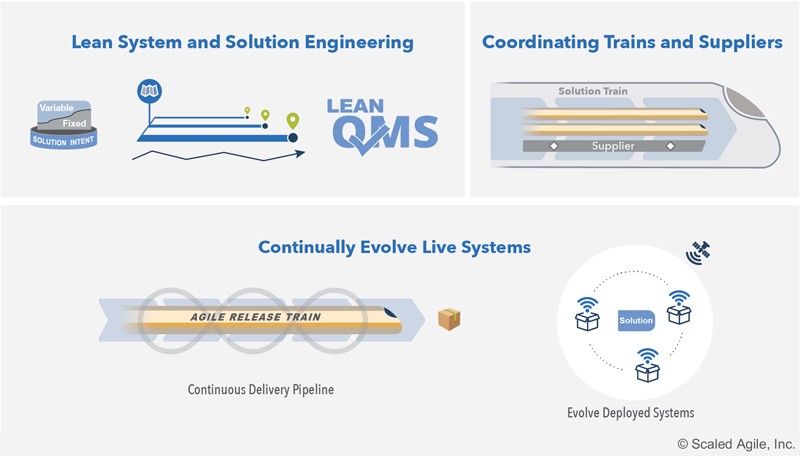
Figure 10. Enterprise Solution Delivery competency
- Lean Solution and Systems Engineering- applies Lean-Agile practices to align and coordinate all the activities necessary to specify, architect, design, implement, test deploy, evolve, and ultimately decommission these systems.
- Coordinating Trains and Suppliers- coordinates and aligns the extended, and often complex, set of value streams to a shared business and technology mission. It uses the coordinated Vision, Backlogs, and Roadmaps with common Program Increments (PI)and synchronization points.
- Continually Evolve Live Systems- ensures large systems, and their development pipeline supports continuous delivery.
5. Lean-Agile Leadership

The Lean-Agile Leadership competency describes how Lean-Agile Leaders drive and sustain organizational change by empowering individuals and teams to reach their highest potential. They do this through leading by example, adopting a Lean-Agile mindset, and lead the change to a new way of working. The result is more engaged employees, increased productivity and innovation, and successful organizational change.
The Lean-Agile leadership article was rewritten and is now organized into the following dimensions:
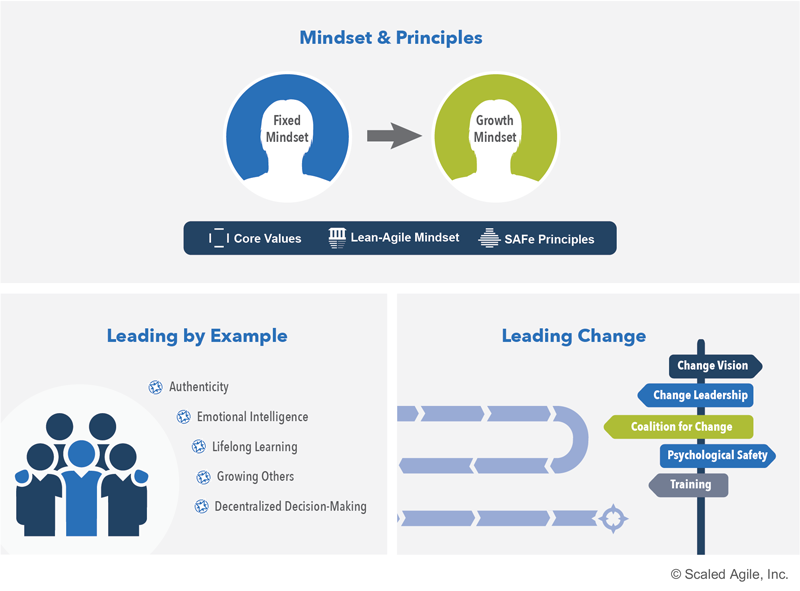
Figure 11. Lean-Agile Leadership competency
- Leading by Example- Leaders gain earned authority by modeling the desired behaviors for others to follow, inspiring them to incorporate the leader's example into their own personal development journey.
- Mindset and Principles- By embedding the Lean-Agile way of working in their beliefs, decisions, responses, and actions, leaders model the expected norm throughout the organization.
- Leading Change- Leaders lead (rather than simply support) the transformation by creating the environment, preparing the people, and providing the necessary resources to realize the desired outcomes.
Customer Centricity and Design Thinking
The customer article has been renamed to Customer Centricity, and the guidance has been expanded to focus on the mindset and impact of customer centricity. This article should be read with the Design Thinking article, which focuses on the tools and practices of implementing design thinking in support of customer centricity.
Customer Centricity
The foundation of the customer-centric enterprise is market and user research (Figure 12) that creates actionable insights into the problems customers face, the solution requirements, and the solution context.
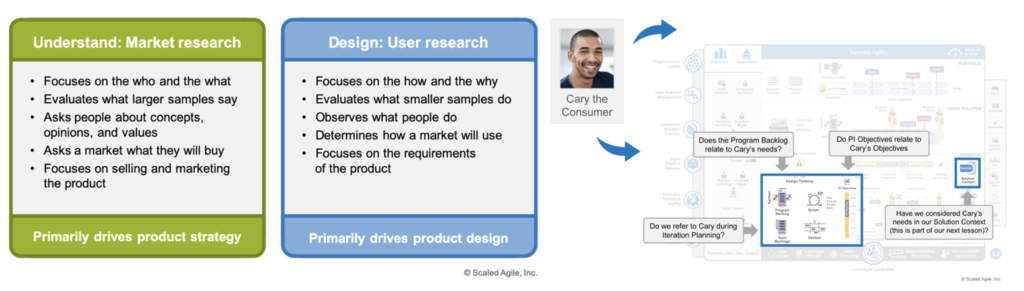
Figure 12. Customer Centricity
Design Thinking
The new Design thinking (Figure 13) article represents a profoundly different approach to product and solution development, in which divergent and convergent techniques are applied to understand a problem, design a solution, and deliver that solution to the market.
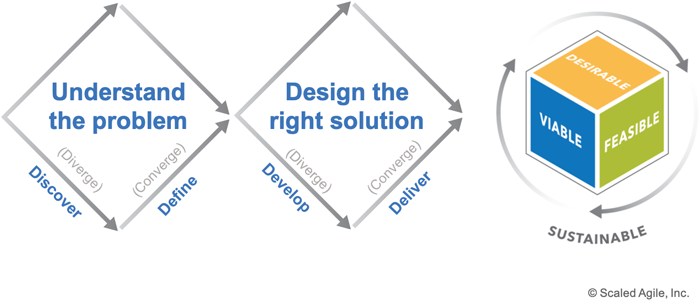
Figure 13. Design Thinking
Design thinking also inspires new ways to measure customer success:
- Desirable: Do customers and users want the solution?
- Feasible: Can we deliver the right solution through a combination of build, buy, partner, or acquire endeavors/activities?
- Viable: Is the way we build and offer the solution creating more value than cost? For example, in a for-profit enterprise, are we profitable?
- Sustainable: Are we proactively managing our solution to account for its expected product-market lifecycle?
SAFe for Business Teams
The enterprise's business teams (Figure 14) are new 'on the train' and participate in delivering and supporting innovative business solutions. They also adopt the Lean and Agile values, principles, and practices that are relevant to their responsibilities and adjust their existing processes accordingly.

Figure 14. SAFe for business teams
Principle#10-Organize Around Value
SAFe Principle #10 - Organize around value (Figure 15) guides enterprises to align their developments efforts around the full, end-to-end value flow. It introduces a 'dual operating system' (Figure 2), which leverages the benefits of a hierarchy, but also provides a network directly organized around value. SAFe's network of value streams organizes the people who need to work together, increase quality, and minimizes delays and handoffs.

Figure 15. New principle # 10 - organize around value
SAFe House of Lean
The SAFe House of Lean graphic has been updated to reflect the new guidance provided in the new and revised core competencies. The more significant changes are highlighted in red (Figure 16). See the Lean-Agile Mindset article for more information.

Figure 16. SAFe House of Lean changes
The SAFe Implementation Roadmap has been updated to include two new courses (Figure 17). Additional changes are also highlighted by the red boxes and are described next.
- Lean Portfolio Management (LPM)
- Agile Product and Solution Management (APSM)

Figure 17. New SAFe Implementation Roadmap changes
SAFe curriculum updating to SAFe 5
SAFe House of Lean

New SAFe Implementation Roadmap
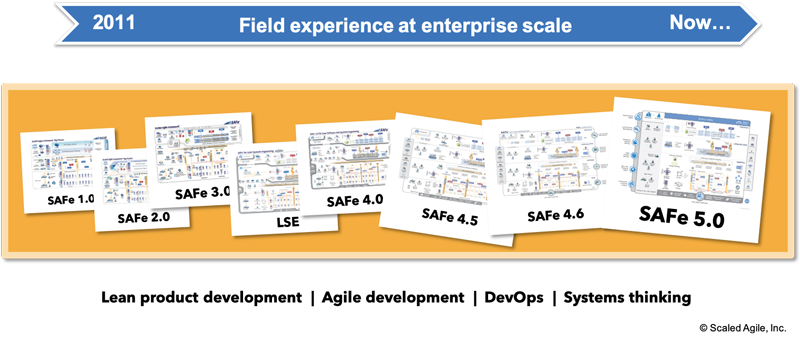
A Brief History of SAFe
Since Scaled Agile announced the SAFe® 5 preview at the Global SAFe® Summit, a lot of people have asked us for a presentation outlining what the new version is all about and the changes from version 4.6 to 5.0. Well, Scaled Agile heard you and we’re excited to announce that our What’s New in SAFe® 5 presentation is now available to download.
Use the deck to inform yourself, your organization, colleagues, and customers about the newest version of the Framework. In addition to providing the why behind business agility, the presentation covers the what of SAFe® 5 Scaled Agile hope this deck gives you the information and guidance you need to start your journey to SAFe®5 and toward business agility.
While Scaled Agile designed this deck for people who know SAFe well, Scaled Agile are also working on another presentation for those of you who want to introduce SAFe® 5 to new audiences.
Stay tuned to the Framework blog for updates. —Stay SAFe
By Inbar and the Framework Team
With five major updates since its initial release in 2011, SAFe has grown with the marketplace as we uncover new and better ways of developing software and systems. Although new versions of the SAFe Big Picture are released only occasionally, the Framework knowledge base is continuously updated with new and improved guidance between releases. Please subscribe to SAFe Updates to stay informed of these important changes. Below is a quick view of the Framework’s history.